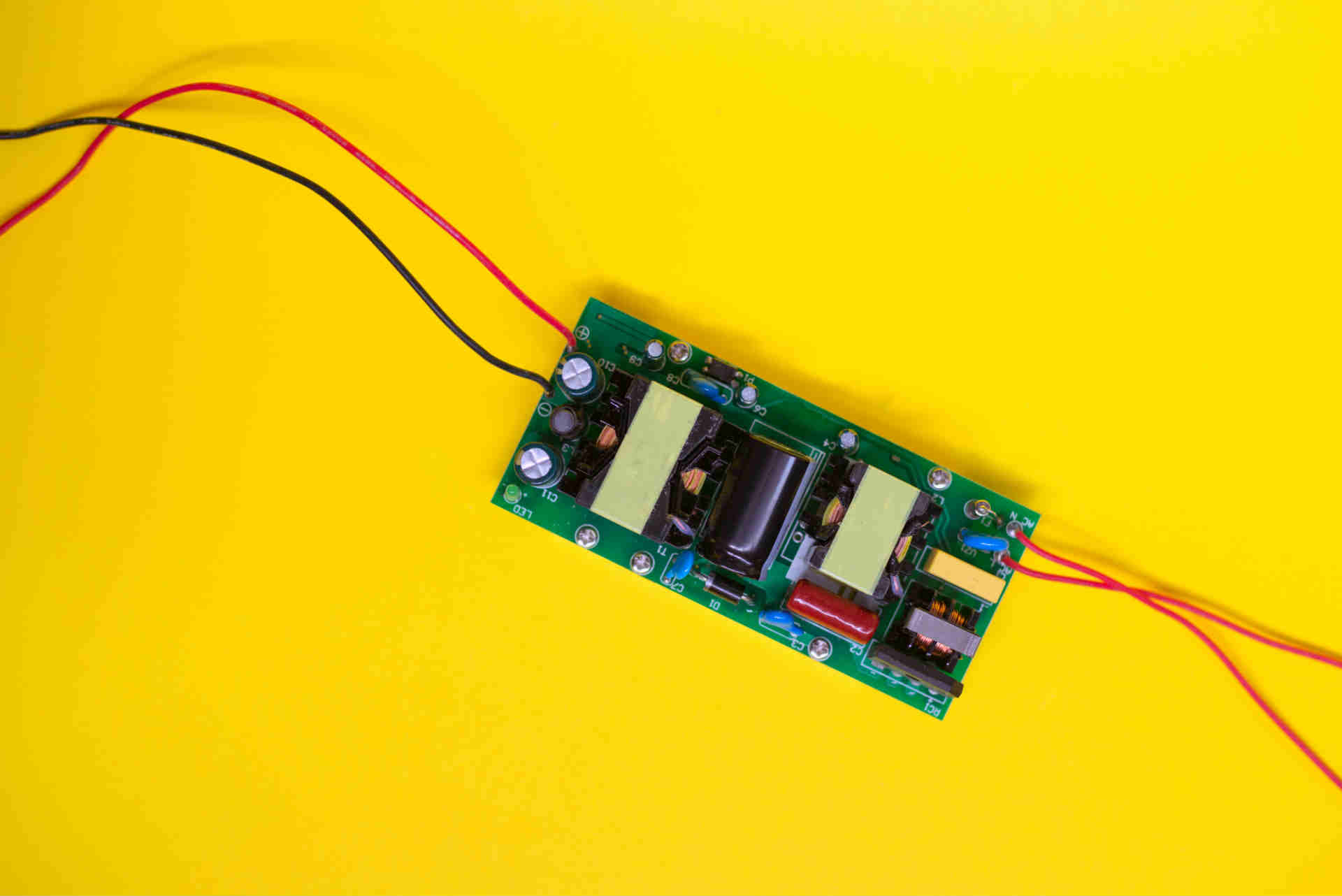
One of the most important elements in the operation of LEDs are the drivers. Unlike traditional lighting, LED lighting does not connect directly to the mains, but rather via a driver that transforms the voltage it receives from the mains and adapts it accordingly to the LED luminaire.
An LED is a solid lamp in itself. It has no filament or gas around it, and no glass capsule to encase it. This type of lighting works in a completely different way, so to fully understand the role of an LED driver it is worth knowing how an LED diode works.
An LED is a semiconductor device that emits light in the visible spectrum when it receives voltage between its two ends. If positive voltage is applied between the two ends, it becomes positively polarised and this is when the light is emitted. So how is an LED powered?
What is an LED driver and why is it so important?
In essence, a driver is a device that converts the alternating current coming from the mains into a direct current of a suitable voltage for the luminaires to work properly. This device regulates the power supply to one or more LEDs. What makes LED Drivers special in relation to a conventional power supply is that they are able to adapt to the changing needs of the LEDs through a constant power supply.

Functions of an LED driver
- Regulating the flow of electricity by ensuring that an LED is always supplied with the correct voltage and current, independent of constant changes in the electrical properties of the LEDs.
- Adjust the voltage supplying the LEDs to supply a constant current in the face of temperature changes that can alter the way the LEDs react to electricity.
How does an LED driver work?
LEDs work with direct current (DC), i.e. constant intensity current in which the movement of the loads is always in the same direction, like batteries, for example. Therefore, if you want an LED light to work in an alternating current (AC) installation, like the ones commonly used, you will need a driver that converts this alternating current into direct current. Without a suitable driver, the LED can overheat or go out of control causing a loss of performance or permanent failure.
The output current of an electrical installation exceeds the power that an LED requires to emit light, so the driver is in charge of reducing it without wasting energy, maintaining a constant current and attenuating the generation of heat. There are two different types of LED drivers depending on where they are installed.
Types of drivers: internal or external
In essence, we can distinguish between two types of driver:
- Internal driver.
- External driver.
When choosing an LED bulb, you should take into account the type of luminaire where you are going to install it, i.e. whether it is in a closed or open luminaire. If it is an open luminaire, there is no problem as the structure itself facilitates heat dissipation. On the other hand, if the support is closed, a space for air flow must be reserved inside the luminaire after installing the LED bulb.
It is recommended that the space we reserve is twice the size of the bulb we are using, if the space is smaller, then it is advisable to use an external driver. And the reason is simple, because by doing so you prevent the heat generated by the driver from being retained inside the luminaire and affecting the operation of the bulb. In any case, the descriptions of the different lighting products indicate when a bulb is not recommended for use in enclosed luminaires.
For domestic lighting, it is common to find internal drivers installed in the LED lights themselves, such as in wall lights and small lamps. On the other hand, high-power LED lights, such as those for industrial use or public lighting, have external drivers that regulate the power of several chips at the same time.

Having a quality driver is essential to help LED lighting achieve its full potential in terms of its lifespan and energy efficiency among other beneficial features.
How to connect an LED driver
Connecting LEDs to a driver is a very simple process. In fact, with integrated drivers such as a light bulb, you don’t need to do anything, it is installed in the same way as a conventional light bulb.
For the most common external drivers, such as downlights, there is a connector similar to a headphone jack that connects to the input of the luminaire on one side and on the other side there are generally two cables (live and neutral) that connect to the mains.
How much energy an LED driver consume?
One of the main advantages of LED drivers over old halogen bulb transformers is that they are much more efficient and quieter devices.
Although drivers are designed to convert alternating current into direct current in the most efficient way, there will always be an energy loss in the process that will be dissipated in the form of heat. To calculate this extra consumption introduced by the driver, it is necessary to know its power factor.
For example, if you have a driver with a power factor of 0.9, i.e. an efficiency of 90%, to supply a 50W spotlight, the total consumption is 50÷0.9=55.555W. Therefore, the consumption of the driver would be about 5.55W.